

Tao Te Ching
Scientists Lineage
To discover something new, we need to let go of our narrow views, our prejudice, our belief systems. If we’re fully convinced, why search for a new and better answer? So almost by definition, scientists personify at least this aspect of our non-thought, wisdom-beyond-words lineages. When the conceptual lid comes off removing status quo religious and cultural moralities and restraints, however; the path toward wisdom and enlightenment is only one of the choices. This list describes scientists who have both opened their creative consciousness as well as - at least most of the time - taken the path of wisdom.
“Science is a bit like the joke about the drunk who is looking under a lamppost for a key that he has lost on the other side of the street, because that's where the light is. It has no other choice.” — Noam Chomsky
“Science, like a general, is identifying its enemies: received wisdom and untested assumptions; superstition and quackery; the tyrants' fear of educated commoners; and, most pernicious of all, man's fondness for fooling himself.” — David Mitchell
People (85)

Shennong 神农 (Shen Nung, Divine Farmer, Emperor of the Five Grains)
2737 – 2697 BCE
“Father of Agriculture” and Traditional Chinese medicine
“Father of Agriculture” and irrigation; inventor of the plow, axe, rake, digging wells, preserving seeds, cultivating grain and the farmer’s market; Chinese history also credits Shen Nung with developing science and the use of herbs for medicine, moxibustion, taking pulses, and acupuncture. Said to have discovered tea, he is also quoted in the I Ching and the Huainanzi. Wandering through remote mountains and plains, he identified and then cultivated rice, wheat and millet; tasted and tested hundreds of herbs, developed the first pharmacopoeia and Traditional Chinese medicine.

Huangdi 國語 (The Yellow Emperor)
2698 – 2598 BCE
Taoist patron saint, founder of Chinese civilization
Considered the initiator of Chinese civilization, ancestor of all Han Chinese and patron saint of Taoism, Huangdi is also credited with first establishing a centralized state, inventing the wheel, the magnet, wooden houses, carts, boats, the bow and arrow, astronomy, the calendar, coined money, weaving silk, dying clothes and the first Chinese character writing system. Parts of Lao Tzu’s chapter 6 may have been quoting him. Dreaming of an ideal kingdom, he successfully devoted his reign to establishing a golden age based on wisdom, natural law, and the power of goodness.

Leizu 嫘祖 (Léi Zǔ or Xi Lingshi)
27th century BCE
Legendary Chinese empress, inventor of silk
A legendary Chinese empress and wife of the Yellow Emperor, Huangdi, Leizu is credited with discovering silkworms when she was having tea and a cocoon fell into her tea. She then learned how to make silk, invented the silk loom, and taught women how to breed silkworms and weave silk fabrics. She was instrumental in helping her husband establish one of the world’s greatest golden ages. China maintained a monopoly on silk production for thousands years and it only spread to Japan c. 300 CE, to the Byzantine empire in 522 CE, and not to Western Europe until the 16th century.

Imhotep
2650 – 2600 BCE
First Western architect, engineer and physician
Considered the first architect, engineer and physician of early Western history, Imhotep invented tools, made great sculptures, and built the first Egyptian pyramids. High Priest, Chancellor, Chief Doctor and Carpenter; he was also revered as a poet and philosopher and was one of the few figures in history born a commoner and deified after his death. "Father of Medicine,” formulator of wise sayings, patron saint of scribes; his legacy and influence helped form the beginnings of ancient Greek culture. His fame continues in modern times disguised in movies, TV shows, comics and video games.
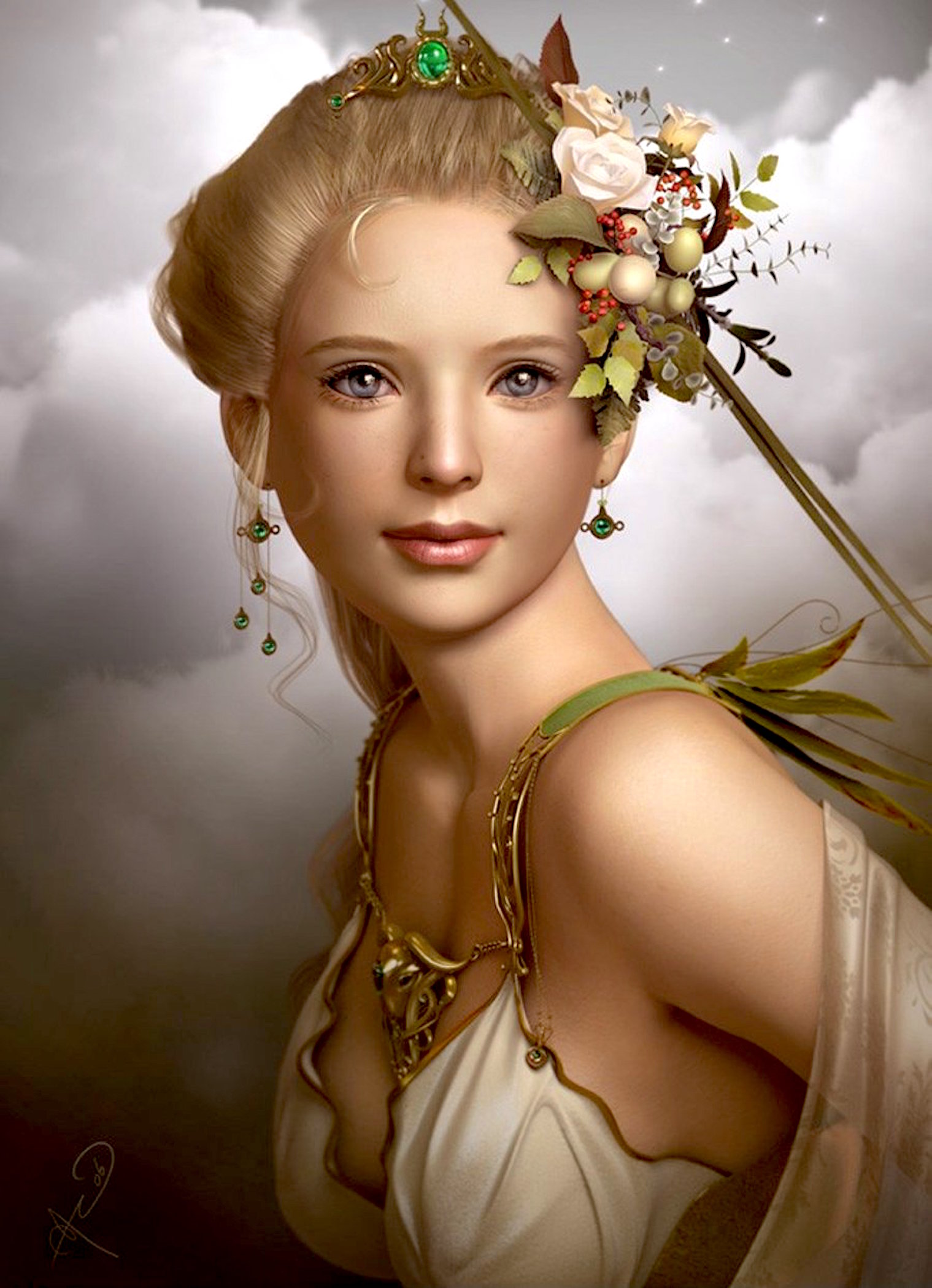

Demeter (Ceres)
c. 2500 BCE
Eleusinian goddess, discoverer of agriculture
“Where smoke, there’s fire” and where a god or goddess, probably real people beginning the symbolism. Like Shennong in China, the Greeks credited Demeter with the discovery of agriculture and like the Chinese Nüwa as the transition from matriarchal to patriarchal society. Assuring fertility with mystic rites and social order as "Law-Bringer;” she predates the Olympian pantheon and with her daughter Persephone is central to the Eleusinian Mysteries, a holy, psychedelic communion celebrating birth, death, and resurrection giving (along with the Egyptian belief in immortality) to Christianity a “weapon with which to conquer the Western world” (Durant).

Hatshepsut (Hatasu)
1507 – 1458 BCE
"The Queen Elizabeth of Egyptian History"
Called by historians "the first great woman in history” and “one of the most powerful women in the history of the world,” Hatshepsut was also one of the most successful and compassionate pharaohs and set the stage for the zenith, the most golden age of Egyptian culture. Credited with the first transplanting of foreign trees, the first use of resin (making a kohl eyeliner), and one of the most prolific builders; she made the tallest surviving ancient obelisk on Earth, buildings not rivaled for a thousand years, and so many statues that almost every major museum in the world includes them.

Thales of Miletus
624 – c. 546 BCE
“Father of Philosophy”
One of the “Seven Sages of Greece,” called the founder of Western Science and “Father of Philosophy,” Thales traveled to Egypt and studied with an Egyptian priest. He then returned to become ”the first Greek mathematician,” history’s first to use geometric deductive reasoning, to have a mathematical discovery attributed, and becoming the first to explain nature without myth or superstition, he set the direction for the golden age of Greek philosophy. Wanting to prove the practicality of philosophy and science, he applied it to business creating the first instance of using options and futures and to politics stopping a battle by predicting an eclipse.

Pythagorus (of Samos)
570 – 495 BCE
"The most influential philosopher of all time"
The ancient Greeks called Pythagoras “the philosopher.” He discovered the numerical relationship between musical notes, the “music of the spheres,” gave geometry its main form, the Pythagorean theorem, and the name cosmos to the world. An elemental influence on Plato (The Republic considered based on the vegetarian, communistic community Pythagoras established) and the first to teach that the world is round and revolves around the sun, his influence extends to all of Western philosophy, Freemasonry, Rosicrucianism, mathematics, architecture, sculpture, art and music. Bertrand Russell considered him the most influential philosopher of all time.

Parmenides
540 – 450 BCE
Grandfather of Western philosophy
Parmenides of Elea Παρμενίδης ὁ Ἐλεάτης (c. 540 - 450 BCE)
Father of Western logic, grandfather of Western philosophy, major influence on the development of science, promoter of the most paradoxical (contrary to appearances) vision of reality, and venerated by Plato and Aristotle; Parmenides taught that our experiences of “reality” are illusory, that the profound oneness of life makes change impossible, existence timeless, and that nothing either dies or is born. In The Way of Opinion, he explains the world of appearances, in which one's sensory faculties lead to conceptions which are false and deceitful. In The Way of Truth, he describes a mystical experience of absolute, unborn reality. These categories parallel our theme of “the words or the sense.”

Anaxagoras Ἀναξαγόρας
510 – 428 BCE
“The Copernicus and Darwin of his age”
An heroic philosopher and scientist in a time with few scientific instruments but remarkable scientific discoveries, Anaxagoras introduced the concept of Cosmic Mind, correctly explained eclipses and why the moon shines, theorized about meteors, thunder, rainbows, the sun, and stars. He developed an insightful theory for the evolution of animal and human life and helped create the foundation for Greece’s most lasting scientific insight, the atomic understanding of matter. Immortalized in literature, he became a character in Goethe’s Faust and was quoted by Socrates, Plato, Seneca, Marcel Proust, and Gore Vidal. His genius was not always appreciated though. Dante placed him in Limbo (the First Circle of Hell) and he was sentenced to death because of teaching that the sun is a mass of fire instead of a god.

Empedocles
490 – 430 BCE
"The father of rhetoric"—Aristotle
Empedocles Ἐμπεδοκλῆς (490 – 430 BCE)
Brilliant orator, physician, poet, vegetarian, magician, pre-Socratic Greek philosopher, and called by Aristotle the father of rhetoric; Empedocles, according to Kingsley, “brought the germs of a new civilization into existence” and became a foundational researcher who set the stage for Euclid and the other early scientists. Also a highly successful politician who helped over through tyrannical and oligarchic governments but then declined offered sovereignty, he was the last Greek philosopher to write in verse. First in the west to describe the four classical elements, he taught the first comprehensive theory of light and vision, anticipated Darwin's theory of natural selection, and believed that all living things reincarnate between humans, animals and plants. Said by Pliny to have traveled to the east and studied with the Magi, Empedocles explained how limited and narrow our perceptions remain while our concepts fool us into believing we understand the whole, how we believe the words without insight into the sense.

Herodotus Ἡρόδοτος
c. 484 - 425 BCE
“The Father of History”
“The Father of History” and first known historian to systematically collect and investigate facts, Herodotus described the purpose of his efforts “to prevent the traces of human events from being erased by time, and to preserve the fame of the important and remarkable achievements.” While the accuracy of his accounts is often questioned, he worked hard to corroborate his stories. From an internationally-minded port city and widely traveled, he describes many of his accounts from an eye-witness perspective. With an overarching theme of civilizations in conflict, he collected oral histories during his travels, thought about their meanings and interpreted them. Not only reporting on ancient science, he also speculated on scientific, cultural, geographical, and historical questions. His role in bringing ancient wisdom into modern understanding is immense.

Mozi 墨子 (Mòzǐ)
470 – 391 BCE
Chinese personification of Newton, da Vinci, and Jesus
Carpenter, precursor to Newton in science, to da Vinci with inventions, to Jesus and Christianity in religion, a politician so provocative emperors burned his books and followers; Mozi taught authenticity and personal insight over dogma and obedience, "universal love,” and the "Golden Rule.” A selfless worker for the good of the others without concern for personal gain, he described inherent basic goodness, benevolence as practical and natural, adversity as beneficial, and government based on talent and merit rather than background and family. Traveling from crisis to crisis in the war-ravaged China of his time, he stopped wars and prevented battles.

Democritus Dēmókritos
460 – 370 BCE
Father of modern science and greatest of ancient philosophers
The "father of modern science,” famed for his atomic theory of the universe, mathematics and geometry pioneer, called by Francis Bacon “the greatest of ancient philosophers;” the famously cheerful Democritus was born into a very rich family but spent almost all his money becoming in his era the most widely traveled going as far as Ethiopia, Persia, and India where he is said to have been exposed to and influenced by Buddhism. Returning without wealth, he devoted himself to a simple life of philosophy, science, music and art creating an influence still with us today.

Aristotle Ἀριστοτέλης
382 – 322 BCE
Famous student of Plato and teacher of Alexander the Great, the first to organize a group to do scientific research, to systemize Western philosophy, to formalize a system of logic and to develop a theory of evolution; Aristotle is considered "The First Teacher" by Muslims and a profound influence on Judaism and Christian theology that extended through the Renaissance and continues today. Though only about one third of his writings remain and much more a proponent of the words rather than the sense, Cicero described him as "a river of gold,” Dante as “the master of those who know,” and through 1500 years of European history, “the philosopher.” He taught virtue as the secret of happiness, politics as the art of compromise between classes, and politically creating a balance between faith and reason, equality and freedom.

Archimedes (of Syracuse)
287 – 212 BCE
Considered the greatest mathematician of ancient times and one of the greatest of all times, Archimedes was also an inventor, astronomer, and engineer frequently called ”superhuman" by Galileo. Some of his inventions include the block-and-tackle pulley system, the odometer, a way to find the value of π, the measurement of a circle and a sphere, the making of a planetarium, and the system of exponents for expressing large numbers. His formulations for uses of the lever and balance remained without improvement until 1586 CE. Featured on postage stamps issued by Germany, Greece, Italy, Nicaragua, San Marino, and Spain; his exclamation “Eureka!” while running naked through the streets of Syracuse after discovering the principle of displacement is the state motto of California.

Eratosthenes ρατοσθένης (of Cyrene)
276 – 195 BCE
Chief librarian of Alexandria, student of the best teachers of his age: the Stoic founder Zeno, the first serious academic Stoic Arcesilaus, the famous poet Calimachus, and grammarian Lysanias; Eratosthenes invented geography (his terms still used today), made the first Western map of the world including parallels and meridians, calculated the circumference of the Earth and the tilt of its axis for the first time, invented leap day, accurately measured the distance from the Sun to the Earth, and founded “scientific chronology.” The first geographer to mention the Chinese, he criticized the Greek chauvinism of describing foreigners as barbarians and recommended judging people as individuals instead of as members of religious, cultural, or national groups.

Lucretius (Titus Carus)
99 – 55 BCE
The greatest Western philosophical poet, a complete evolutionist, writer of the “loftiest poetry that any age has known” and the “most marvelous performance in all antique literature” (Durant); Lucretius described religion, the universe, and medicine from a rational point of view without superstition, faith, or dogma. An Epicurean with allegiance to only Venus and the power of love, he left behind all other gods and proposed a scientific understanding of the world including atomic theory and evolution. A huge influence on ancient times, people like Virgil and Horace; he also inspired Enlightenment era people, humanism, Thomas Jefferson and modern psychology.

Al-Kindi (Abu Yūsuf Yaʻqūb ibn ʼIsḥāq aṣ-Ṣabbāḥ)
801 – 873 CE
While European countries were still stuck in the dark ages of almost universal superstition and ignorance, Al-Kindi - knows as “father of Arabic philosophy” - precipitated the “Moslem Enlightenment,” one of the true golden ages of human history, a time that threw off its dogmatic shackles of uncritical belief and advanced science, direct experience unfettered by external sources, understanding of the sense and not just the words. A famous historian, physician, polymath, musician and mathematician; he brought Hellenistic wisdom into the Muslim world and shocked his contemporaries by appreciating Christianity.

Avicenna أبو علي الحسين بن عبد الله بن الحسن بن علي بن سينا (Ibn-Sīnā)
980 – 1037 CE
Persian polymath, spur to the Islamic Golden Age, poet, doctor, scientist, philosopher and one of the most significant thinkers and writers of his time; Avicenna wrote over 450 books one of which became the standard medical text for European universities up until as late as 1650. With influence from Plato and Aristotle, he clarified the distinction between the words and the sense, taught a spiritual path beyond motivations of hope and fear, reconciled the conflict between reason and faith, and his works according to Will Durant, “mark the apex of medieval thought and constitute one of the major syntheses in the history of the mind.”

Shen Kuo 沈括 (Mengxi)
1031 – 1095 CE
Greatest scientist of his age, statesman, inventor, poet, finance minister, horticulturalist, engineer, art critic, diplomat, military general, musician, and commentator on ancient Daoist texts; Shen Kuo discovered the magnetic compass needle and the concept of true north which revolutionized navigation 400 years before known in Europe, popularized Bi Sheng’s invention of moveable type 400 years before Gutenberg, researched and described climate change, made the first raised-relief map, described UFOs and beneficial insects, re-discovered an ancient Chinese surveying tool unknown in Europe until 1321. Politically aligned to Wang Anshi, he was impeached, exiled and spent his older years with the "nine guests" — playing music, weiqi (Go), Chan meditation, painting, tea, alchemy, poetry, conversation and wine.

Arwa al-Sulayhi (Al-Malika al-Ḥurra)
1048 – 1138 CE
The stellar example in Muslim history of an independent queen; Arwa ruled Yemen, was the greatest leader during the Sulayhid Dynasty, and was - for the first time in the entire history of Islam - a woman given the title of hujja, the highest status in Islam. Extremely beautiful, intelligent, scholarly, brave, and powerful; she studied science, poetry, history, completed practical and beneficial infrastructure projects, supported agriculture, and built many schools. Her direct lineage continues today in both Yemen and India.

Omar Khayyám
1048 – 1131 CE
Persian Astronomer-Poet, prophet of the here and now
In the west most famous for his poems but Omar Khayyam was also a political advisor, “philosopher of the world,” one of the most influential scientists of his era, “one of the greatest mathematicians of medieval times,” and “without equal in astronomy and philosophy.” A prophet of the here and now, mystical Sufi teacher and free-thinker who rejected theology; he reformed the Persian calendar to a form more accurate than our own today, wrote the most important until modern times book on algebra as well as many others on astronomy, geography, and mechanics. His poems—known as the Rubáiyát—not only rejected Islamic belief and Christian morality, but the nature of religion itself.

Hildegard of Bingen
1098 – 1179 CE
Circumventing her times’ strong prejudice and bans against women's social, artistic and theological participation, Hildegard became a famous writer, composer, botanist, philosopher, visionary, Christian mystic and the founder of scientific natural history in Germany. The first Westerner credited with describing the healing powers of food and corresponding with the political, religious, and scientific leaders of her day (popes, emperors, saints and scientists), she used her influence to combat corruption, promote spiritual insight, holistic healing, the arts, and women’s role in the world

Averroes, Ibn Rushd ابن رشد
1126 – 1198 CE
Polymath, famous Islamic philosopher and scientist, theologian, and physician; Averroes took the position that the Koran and sacred writings were allegories and not to be taken literally. Arguing for an understanding deeper than just the literal meaning of texts, he popularized Aristotle and started a major Jewish and Christian philosophical movement but didn’t become influential in the Muslim world until the 19th century. In fact, during his lifetime, all his books that could be found were burned, he was removed from his positions, and exiled. Dante described him as he "who made the Great Commentary,” Chaucer listed him as a great medical authority, Raphael painted him into a fresco in the Apostolic Palace in the Vatican that depicts major philosophers, Borges featured him in one of his books, and a plant genus, a lunar crater and an asteroid were named after him.

Guo Shoujing 郭守敬 (Ruosi, Kuo Shou-ching)
1231 – 1316 CE
One of the history's most influential scientists
Most highly regarded Chinese engineer, astronomer, mathematician of all time; a child prodigy and Kublai Khan’s chief science advisor, Guo Shoujing developed a calendar used for 363 years, the longest use of one calendar in all of Chinese history and the foundation for the Gregorian calendar that is still the world’s most used calendar. Spreading an approach called "evidential learning,” he became the leading influence on the development of Chinese science. He invented astronomy tools that calculate the accurate length of a year, an astrological compass using the stars instead of magnets, perfected watches and clocks that greatly increased accuracy, and perfected irrigation and reservoir techniques that increased harvests for hundreds of years.

William of Ockham
1287 – 1347 CE
Major intellectual figure during medieval times, Franciscan friar at the center of the biggest political controversies of his era, and famous for his principle now called Occam’s razor; William of Ockham’s commentaries were condemned by a council of bishops and he was commanded to defend himself at a papal court. Instead, he fled the country, took refuge with the Holy Roman Emperor, and was excommunicated. One of the first to encourage a strong separation between church and state, a liberal democratic ideology, and social contract theory; his Occam's Razor theory became a small-is-beautiful, less-is-more foundation for modern science and natural philosophy.

Leonardo da Vinci
1452 – 1519 CE
One of the most talented people to have ever lived, original “Renaissance Man,” father of paleontology, ichnology, and architecture; with a passionate curiosity and interest in everything, da Vinci’s genius extended to science, music, mathematics, engineering, painting, architecture, sculpture, anatomy, geology, astronomy, botany, history, and cartography. Remarkable inventor, mystical pantheist, vegetarian, savior of caged birds, and exemplar of journey-without-goal, he wrote over 5000 pages but didn’t finish one book, many of his commissions, even some of his greatest paintings, and claimed that one of the his most famous paintings, The Mona Lisa was incomplete.

Copernicus, Nicolaus
1473 – 1543 CE
Creator of one of history's greatest revolutions
From our point of view, such a simple and obvious proposition—that the Earth rotates around the Sun. At his time and place in history, however, Copernicus created one of the most far-reaching revolutions of understanding in the history of the world. Mathematician, astronomer, physician, translator, diplomat, economist, polyglot and polymath; his celestial theory threatened the powerful Catholic Church so much it was considered an atheistic blasphemy and because Galileo agreed with it, he was incarcerated for the last nine years of his life. An early humanist, he also developed an important economic concept and theory of money, translated poems from Greek to Latin, and even became an effective and influential government official.

Agrippa (Heinrich Cornelius Agrippa von Nettesheim)
1486 – 1535 CE
Historian of the occult and early, important influence on science
Physician, soldier, polymath, theologian, and the most important magic occultist of his age; Agrippa pushed hard on the ideological and religious belief boundaries of his time and, as a consequence, found himself at odds with inquisitors, banished, imprisoned, and continually threatened. His books shifted historical trends. One attacking the contemporary state of science influenced writers like Goethe, Montaigne, and Descartes. A book he wrote in 1529 argued for the moral and spiritual superiority of women and his 3-volume Occult Philosophy (printed 1531-1533) became a foundational resource for Occultists then and now. In Mary Shelley's famous novel, his writing are described as a major influence on the young Victor Frankenstein and he's similarly cited in works by Christopher Marlowe, Søren Kierkegaard, and J. K. Rowling.

Paracelsus (Theophrastus von Hohenheim)
1493 – 1541 CE
Revolutionary, shamanistic alchemist
“Father of toxicology,” alchemist, medical revolution pioneer, and astrologer; Paracelsus was venerated by the Rosicrucians, intensively studied by Carl Jung, and revered by future physicians who universally recognize his medical contributions. He criticized the popular purging and bloodletting techniques of his time as well as the practices of applying cow dung to wounds. He revolutionized medicine by conceiving clinical diagnosis, promoting the keeping of wounds clean, anticipating Germ Theory, using specific instead of cure-all medicines, doing medical experiments on animals, treating mentally ill as treatable instead of possessed by evil spirits, discovering that syphilis is contracted by contact, that “poor blood” can be improved with iron, and creating the terms "chemistry," "gas," and "alcohol.” Jung carried on his work of alchemy as symbolic language expressing unconscious and innate psychological influences.

Giordano Bruno
1548 – 1600 CE
Giordano Bruno (1548 – 1600)
Like Galileo, a "martyr of science," Dominican friar, Epicurean poet, cosmological mathematician; Bruno fled his monastery and wandered through France and Italy teaching. Burned at the stake by the Roman Inquisition for his scientific, pantheistic, and Epicurean views; Bruno first described stars as distant suns with planets of their own, championed the Copernican view that the earth is not the center of the universe, and taught the dangerous view that likewise people and our civilizations are not the center of the cosmos but only a tiny part of something much larger. This led to an 8-year trial, his torture and death but also a strong foundation for the newly emerging sciences and the openness to free thought.

Francis Bacon
1561 – 1626 CE
“Father of the scientific method,” Lord Chancellor of England, orator, jurist, and philosopher; Francis Bacon represents a huge step in the evolution of consciousness but not before indulging in a sybaritic lifestyle, being charged with 23 cases of corruption, being banned from Parliament and imprisoned in the Tower of London. In his ex-con life, he undermined the strength of religion, railed against tradition and authority, became “the most powerful and influential intellect of his time,” warned of the rich getting too rich as a cause of social disease and revolt, the likelihood of new inventions causing more harm than help, and championed the rise of reason and science that brought about our modern world.

Galileo
1564 – 1642 CE
Arrested by the Inquisition for the last 9 years of his life but called by Einstein “the father of modern science;” books banned by the Catholic Church but called by Stephen Hawking responsible for the birth of modern science; condemned and persecuted by conservative contemporaries but called by Grotius “the greatest mind of all time;” Galileo – though living in a time when “heretics” were burned at the stake – raised the status of science, with his telescope designs demonstrated the universe’s immensity, and helped science separate from both philosophy and religion.

Blaise Pascal
1623 – 1662 CE
One of the greatest French writers of all time
Theologian, inventor, physicist, philosopher; Pascal invented the mechanical calculator, set up the first bus line moving passengers, became one of the greatest French writers, and developed probability theory which has become critical to economics, actuarial science, and the way we understand decision-making and risk. Although he identified with Jansenism which emphasized original sin and human depravity and frequently fixated on religious dogma, his understanding extended to a deep realization of our strong propensity toward projection and self-deception as well as a philosophy of cutting through this kind of deceit and duplicity. His significant scientific contributions led to attaching his name to a programming language, a unit of pressure, and a hydrostatic law. Will Durant called one of his writings, "the most eloquent book in French prose.”

Isaac Newton
1642 – 1726 CE
Natural philosopher, mathematician, astronomer, theologian, author and physicist, and one of the most influential scientists of all time; Newton built the first practical telescope, made critical discoveries in the field of optics, developed calculus, made numerous scientific discoveries and also studied alchemy. He established science over faith as the most profound influence on modern thought and his discovery of gravitation revolutionized the study of astronomy. He established the laws of motion and mechanics that became a platform for the modern miracles of science. Exemplifying Gracian’s dictum, “All giants are really dwarfs,” stories of Newton’s absentmindedness proliferate. Asked to boil an egg for 3 minutes, he put his watch in the water and stared at the eggs. He would do things like go upstairs to change for a formal dinner but instead get undressed and go to bed. Voltaire considered him one of the greatest men who have ever lived.

Leibniz (Gottfried Wilhelm (von) Leibniz)
1646 – 1716 CE
Polymath, philosopher, mathematician, scientist, engineer, lawyer, university president and “best-of-all-possible-worlds man”; Leibniz developed calculus, invented components that became the first calculator, and refined the binary number system that became the foundation for digital computers. His writings on law and politics and call for a European confederation inaugurated the European Union. One of the first major European intellectuals to study Chinese culture and philosophy, he read Confucius, studied the I Ching, and integrated Chinese wisdom into both his philosophy and physics. It led to his “law of continuity” that linked the nature of everyone—plants, humans, animals, both the organic and inorganic worlds—, created a theoretical foundation for evolution, and envisioned a non-dual calculus of understanding reality.

Emanuel Swedenborg
1688 – 1772 CE
Scientist, mystic, influential philosopher
A scientist, philosopher, theologian, inventor, and mystic; Swedenborg began his career as a genius-level scientist and later—detesting the materialism of his academic life—experienced visions and became a highly influential and mystical theologian. He was the first to identify nerve cells, identify the brain's cortex, and pioneered many discoveries in magnetism, phosphorescence, and brain function. His mystical visions described visits to heaven and hell, conversations with spirits from the moon, the planets in our solar system as well as with those from planets further away. His influence spread throughout Europe and into modern times through figures like William Blake, Coleridge, Emerson, Browning, and several Christian denominations.

Benjamin Franklin
1706 – 1790 CE
Beginning his adult life as a penniless runaway, Franklin became one of the world’s most admired people. He was a founding father, diplomat, scientist, philosopher, businessman, inventor, and the politician most responsible for winning the Revolutionary War. His inventions included the lightning rod, bifocals, the Franklin stove, and he helped start many new civic organizations including voluntary fire departments and paid police forces. He recreated the slogan/quote tradition of Aesop and Atisa that we continue in our “Comments” link.

Diderot
1713 – 1784 CE
Philosopher, art critic, scientist, and writer; Diderot was imprisoned in solitary confinement for his philosophical views and mainly only known for his plays and encyclopedia during his lifetime. His rival Rousseau though believed posterity would give him the same respect as Aristotle and Plato and he was later admired by Goethe, Schiller, Balzac, Zola, and Schopenhauer. He was Karl Marx’s favorite prose writer and Comte called him the “foremost intellectual of an exciting age.” He worked on the Encyclopédie as a way of giving power to the common person and emphasized religious tolerance, freedom of thought, the value of science, and—threatening the French aristocracy—maintained that the main purpose of government should be benefiting the common people.

Thomas Jefferson
1743 – 1826 CE
American founding father, main author of the Declaration of Independence, Virginia governor, first Secretary of State, US Vice President and one of America’s greatest presidents; Jefferson negotiated the Louisiana Purchase almost doubling the size of the country and wrote a book considered the most important American one written before 1800. President of the American Philosophical Society, mathematician, architect/designer of the Virginia State Capitol and Monticello, University of Virginia founder, avid horticulturalist and farmer, naturalist deeply interested in birds, inventor of an important new plow design as well as the swivel chair, and speaker of more than 8 languages; he exemplified the ideal of a true Renaissance Man. Although he owned hundreds of slaves, as a young lawyer he defended freedom-seeking slaves, signed an act prohibiting their importation in 1807, and is believed to have secretly “married” and had children with a black woman, Sally Hemings. Always in debt with cash flow problems from continual experiments and pushing on the boundaries of the possible, his creative spirit never died.

Goethe, Johann Wolfgang von
1749 – 1832 CE
Though a literary celebrity at 25 and most well known for his novels and poems, Goethe was also a natural philosopher, diplomat, civil servant, geologist, and scientist who developed a theory of color, inspired Tesla’s discovery of alternating current and whose early work on evolution influenced Charles Darwin. A freethinker who blended Christianity with pantheism, humanism, and other esoteric traditions, he became a major influence on Hegel, Schopenhauer, Kierkegaard, Nietzsche, Hesse and Jung. He authored some of the greatest novels ever written and his poems were set to music by Mozart, Beethoven, Schubert, Brahms, Liszt and many others. Continuously creating for 82 years, his wisdom deepened and merged into a culture we take for granted today.

Arthur Schopenhauer
1788 – 1860 CE
Though mainly unnoticed during his life, after he died Schopenhauer’s work had a huge impact on psychology, literature, art, philosophy, music and science. He was one of the first Western thinkers to affirm major aspects of Eastern philosophy. He called himself a Buddhist and compared his philosophy to basic Buddhist teachings. Einstein extolled Schopenhauer’s life-long influence and he was also respected and emulated by people like Nietzsche, Tolstoy, Freud, Jung, Joseph Campbell and Thomas Mann. His influence continues today into fields like modern evolutionary psychology.

John Stuart Mill
1806 – 1873 CE
One of the most influential thinkers in history, Mill learned Greek at 3 years old, studied Euclid and Latin at 8, Plato at 10, logic and Aristotle at 12, Adam Smith and political economy at 13, chemistry and zoology at 14, and by 20 was suicidal only to be saved by the poetry and inspiration of William Wordsworth. He promoted individual freedom over state control, economic democracy over capitalism, the environment and quality of life over unlimited growth, taxing unearned income high and earned income not at all. He linked freedom with self-improvement, worked to end slavery, and was one of the first in his time to advocate equality for women.

Charles Darwin
1809 – 1882 CE
Revolutionary scientist, one of the most influential characters in human history, and originator of the theory of evolution and natural selection; Charles Darwin generated a scientific consensus that recast humanity’s understanding of itself. Following his father’s decisions, he became a failure in his early academic efforts, a failure in his studies to become a doctor, and a failure in his career as a clergyman because of his intense interesting in beetles and entomology. He traveled to remote islands studying coral reefs, barnacles, animals, fish, insects of all kind and was “struck with the variability of every part in some slight degree of every species.” Unlike Thoreau’s book Walden that didn’t sell enough copies to cover the paper cost, Darwin’s book, The Origin of Species sold out on the first day in print launching a debate that soon led to a dual between scientists and became a controversy that continues today. He studied earthworms for 40+ years and this became the topic of his last book which he wanted to write quickly "before joining them.”

Karl Marx
1818 – 1883 CE
A journalist, philosopher, scientist, and “true founder of modern sociology” and social science; both critics and followers rate Marx as one of the most influential people in all history with a profound impact on world politics, intellectual thought, sociology and economics. A philosopher for the poor and middle classes, he described the economic conflicts of interest that alienate and polarize society between the working classes and the plutocracy. Distorted, corrupted and used by Lenin, Trotsky, Mao, and many other totalitarians; appreciated, developed, and applied by progressive political parties, labour unions, intellectuals, and artists; he brought the scientific method into politics and social theory as well as a powerful alternative to the dehumanizing aspects of capitalistic industrialization. Though questionable in many ways, his work produced a practical and powerful balancing of economic extremes, the exploitation of labor, and the corruption of politicians by the rich. Though more known for his critiques of capitalism, he also appreciated its positive impact on increased productivity, technological progress, and scientific breakthroughs.

Thomas Edison
1847 – 1931 CE
America's greatest inventor
“America's greatest inventor,” businessman, and entrepreneur; Edison set up the world’s first industrial research laboratory, first film studio, and held in his name over 1,100 US and foreign patents in many fields including electric power, communications, and motion pictures (his film studio made almost 1,200 films.). Some of his most influential inventions include the light bulb, phonograph, motion picture camera, the fluoroscope, the tasimeter, and the nickel-iron-battery. Henry Ford was a neighbor and employee who Edison helped with his business ventures. A victim of nepotistic seductions, Edison had to take his son to court for using their family name to promote scams, snake-oil products, and fraudulent ventures. He joined Blavatsky’s Theosophical Society, became a strict vegetarian, and promoted nonviolence.

Sigmund Freud
1856 – 1939 CE
Dismissed and laughed at because of his more outlandish theories, it’s too easy to overlook Freud’s many deep insights. Founder of psychoanalysis and inspiration/influence for many of the important psychologists who came after him including Jung, Adler, Erich Fromm, Wilhelm Reich, and Fritz Perls; he developed many techniques and understandings for treating mental illness—ideas like free association, transference, the Oedipus complex, repression, libido, a theory of the unconscious, and an id-ego-super-ego psychic structure. Fromm—though critical in many ways—described Freud (along with Marx, and Einstein) as an "architect of the modern age,” believed he permanently changed the way we understand human nature, but thought psychoanalysis quickly became corrupted. Although such a famous name today, during his lifetime Freud shared some of the obscurity common to most history-changing people. His influential book, The Interpretation of Dreams (1900) only sold 351 copies during the first 6 years after publication.

John Dewey
1859 – 1952 CE
The "Second Confucius"
American philosopher, psychologist, one of the original 34 signatories of the first Humanist Manifesto, major voice for progressive education and academic freedom; Dewey is considered the “epitome of liberalism,” “one of the fathers of functional psychology,” leading proponent of hands-on learning, and a powerful advocate for democracy. Writing 40 books and over 700 articles in 140 journals, he helped establish the NAACP, supported immigrants, and the women’s suffrage movement. He worked closely with Albert Einstein, Bertrand Russell, Karl Jaspers, Henri Bergson, Martin Buber, and George Santayana; established a college where the faculty included Buckminster Fuller, Paul Goodman, and the Beat Generation "Black Mountain Poets.” One of his students, B.R. Ambedkar, became one of the founding fathers of independent India. President of the League for Industrial Democracy, he refuted the influential Walter Lippmann views on the need to manipulate democracy by using journalism as propaganda. He lived in China during 1919-1922 giving nearly 200 lectures to thousands Chinese audiences who described him as "Second Confucius.” Returning, he gave lectures in the USA discussing the teachings of Laozi.

H. G. Wells
1866 – 1946 CE
A father of science fiction and One World Government apostle
Social critic, journalist, prophetic futurist, and “A father of science fiction”; Wells—a prolific writer of novels, social commentary, and history—wrote more than 100 books. He envisioned the World Wide Web, nuclear weapons, satellite television, mass surveillance, and many other un-invented but now common technologies. He also explored both the positive an negative ways of integrating them into civilization. An outspoken socialist and proponent of equality and human rights, Wells had a strong influence on his friend Winston Churchill who peppered his speeches with Wells-quotes. Nominated for the Nobel Prize in Literature four times, his influence extended to almost all modern science fiction writers. A strong believer in the need for us to become citizens of the world under a One World Government, he helped create the UN-adopted Universal Declaration of Human Rights. He worked hard on the creation of the League of Nations but disappointment with its effectiveness and inability of politicians to elevate the common-world good over their personal benefits led to his conjecture that it might be better for another species to replace humanity.

Madame Curie (Maria Salomea Skłodowska)
1867 – 1934 CE
The first woman to win a Nobel Prize, to win one twice, and the only person ever to win the Nobel Prize in multiple sciences; Madame Curie’s work was “epoch-making” - a huge influence shaping modern times. Though revolutionizing physics and chemistry, she maintained her honesty and moderate life style often refusing honors, insisting monetary awards be given to institutions rather than to herself, and (like Ben Franklin) refusing to patent many of her inventions so that they would be more widely available. Albert Einstein said she was most likely one of the only people in the world who could not be corrupted by fame.

Albert Schweitzer
1875 – 1965 CE
An authentic Christian who didn't hesitate to criticize Christian extremism and hypocrisy, who genuinely practiced his faith by effective humanitarian work in Africa, and who realized a mystical and scientific union of individual and environment; Albert Schweitzer conveyed a deep reverence for all life and taught how destroying our environment is also destroys ourselves. Considered the greatest humanitarian of his day, he gave up a comfortable life as a professor and scholar to become a medical missionary in some of the world's most poverty-stricken places in Africa. After receiving the Nobel Peace Prize in 1952, he gave what many consider one of the best speeches ever given. His work against developing the atomic bomb, however, brought him under FBI/CIA scrutiny, public criticism, and the loss of financial support.

Carl Jung
1875 – 1961 CE
Insightful shamanistic scientist
Psychic adventurer, fearless explorer of the unconscious, uncompromising guide to realms beyond conventional mind; Carl Jung ransacked visions, penetrated to the heart of obscure symbols, brought world culture further along the path of evolutionary consciousness. Bringer of eastern wisdom into Western culture, Jung influenced psychiatry, anthropology, archaeology, philosophy, literature, and religious studies and wrote introductions to books like the I Ching, Secret of the Golden Flower, and D. T. Suzuki’s An Introduction to Zen Buddhism. He founded analytical psychology based on what he considered the central process of human development and a central theme in the Tao Te Ching: integrating opposites.

Albert Einstein
1879 – 1955 CE
Although he made his name synonymous with genius as the father of modern physics and his E = mc2 became ”the world's most famous equation,” Einstein remained humble and unassuming. Although winning a Nobel Prize and writing over 30,000 documents, he didn’t let himself be seduced by fame and fortune but championed civil rights, non-violence, and - like Chuang Tzu and other famous Taoists - refused political honors including becoming the president of Israel. He worked hard for checking the power of nation states with a democratic global government, believed in a pantheistic god, and as an avid violin player said, “I often think in music.”

Teilhard de Chardin
1881 – 1955 CE
Philosopher, geologist, Jesuit priest and paleontologist, Chardin traveled extensively across China and helped discover Peking Man. Although frequently condemned and censored by church officials and his writings banned, later popes, cardinals and theologians praised him and his ideas. Similarly reviled and revered by scientists and described as everything from a “charlatan” to “one of the century’s most prophetic thinkers,” his life manifested the cutting edge of consciousness evolution he described so clearly.

Marie Bonaparte
1882
Princess, psychoanalyst, sex scientist
Princess of Greece and Denmark, author, psychoanalyst, granddaughter of Napoleon’s younger brother and the main Monte Carlo real-estate developer; Marie Bonaparte used her wealth to help Freud escape from Nazi Germany as well as significantly increase the popularity of psychoanalysis. Because of multiple phobias and hypochondria when she was young, she spent much of her time alone reading, studying, and working with the scientific method. This research continued after her marriage and multiple affairs failed to give her orgasms and she did many studies that finally brought her to Freud and his famous comment to her, "The great question that has never been answered and which I have not yet been able to answer, despite my thirty years of research into the feminine soul, is 'What does a woman want?’”. A practicing psychoanalyst, she founded the French Institute of Psychoanalysis, translated Freud’s books into French, wrote several of her own on psychiatry as well as a biography and commentary on Edgar Allan Poe.

John Maynard Keynes
1883 – 1946 CE
Revolutionary economist credited with saving capitalism
One of the most influential economists of all time, founder of modern macroeconomic theory, most effective strategist in ending the great depression, and leading representative of modern liberalism; Keynes became one of the most important and influential thinkers of the 20th century. Promoting the—at the time—radical idea that governments should spend money they don't have may, he helped jump-start the world’s economies out of depression and into history’s most affluent periods. Challenging the prevalent economic theories of Adam Smith, most of the developed world adopted his theories, government policy focused on demand instead of supply, prosperity spread. Attacked by monetarists like Milton Friedman in the 1970’s his recommended policies fell from favor which led to the the 2007-8 financial crisis until they were re-adopted.

Will Durant
1885 – 1981 CE
Philosophy apostle and popularizer of history's lessons
Apostle for philosophy, Catholic priest vocation drop-out, socialist reporter, librarian, professor who quit so he could marry his much younger 15 year-old student who became his 68-year married wife; Durant became not just an ivory-tower intellectual and academic but someone who put the lessons of history into practical lessons useful for average people. He worked for women’s right to vote, equal wages, better working conditions for American labor, and wrote a "Declaration of Interdependence,” that was read into the Congressional Record and started a movement against racial intolerance 10 years before the Civil Rights Movement. Writing “the most successful historiographical series in history,” and awarded a Pulitzer Prize for literature as well as the Presidential Medal of Freedom, he critiqued the West’s “fatal error of perspective:” Eurocentrism, intolerance and provincialism.

Robert Hutchins (Robert Maynard Hutchins)
1899 – 1977 CE
An educational philosopher whose time has arrived; Robert Maynard Hutchins was University of Chicago president, Yale Law School dean, Editor In Chief of the Great Books of the Western World, and a leading proponent of secular perennialism—nonspecialized and nonvocational
education based on discovering the “sense” rather than relying on just the words, on principles not just facts. Encouraging deeper understanding, prioritizing thinking for ourselves, and attacking superficial focus on entertainment and the narrow “trade school” approach to education; he eliminated varsity football at the University of Chicago and implemented novel educational programs based on the Great Books and Socratic dialogue. In later life he ran the Ford Foundation and channeled huge sums into programs for adult education, to train teachers, and to spread liberal arts. One of these became PBS.

René Dubos
1901 – 1982 CE
Influential scientific environmentalist
Microbiologist, leading humanist and influential environmentalist; Dubos wrote 32 books including a Pulitzer Prize winner. Creator of the famous phrase, "Think Globally, Act Locally," he empowered and entrusted individuals, local, and small organizations making needed changes rather than relying only on large, impersonal, and out-of-touch institutions. He argued that only local, small-scale organizations can clearly see and respond to their "unique physical, climatic, and cultural contexts." He balanced this sentiment, however, with an emphasis on need for communication with a world order conscious of environmental priorities. While not ignoring our immense global challenges, he conveys an optimistic, positive, and realistic approach.

Margaret Mead
1901 – 1978 CE
Cultural anthropologist, creator and exemplar of the Jewish mother stereotype, feminist movement cornerstone, husband of Gregory Bateson, mother of Mary Catherine Bateson; Margaret challenged prevailing views about race and intelligence, about traditional sexual mores, about the false identifications that seemingly separate human unity by fixating on visible but insignificant cultural displays. Her work significantly advanced the evolution of a one-world vision and the importance of us all becoming “citizens of the world.” President Jimmy Carter awarded her the Presidential Medal of Freedom in 1979.

Karl Popper
1902 – 1994 CE
Major Philosopher of Science
Social commentator, philosopher, and academic; Popper grew up in an academic household. His parents were good friends of Freud's sister and his father was a true bibliophile with as many as 14,000 books in his personal library. During his student years, he became very interested and supportive of Marxism until police shot 8 of his unarmed friends. That led him to a life-long support of social liberalism and his creation of an evolved philosophy of science. One of his students—George Soros—became a philanthropic billionaire and now support a think-tank dedicated to Popper's influence. Rather than fixating on just one point of view, he worked to reconcile diverse ideas from socialism, libertarianism, social democracy, traditional liberalism and conservatism.

Gregory Bateson
1904 – 1980 CE
Poet-philosopher, deep thinker, anthropologist, and developer of a "meta-science;” Bateson established double-bind theory, helped apply systems theory to the social science, and was part of the core group that developed cybernetics. While married to Margaret Mead, he worked in South Pacific islands on anthropology and during World War II on black propaganda which led to a marriage-fatal disagreement with his wife on the use of science and technology in social planning. Describing 20th century history as a malfunctioning relationship based on betrayal and hate, he posed the development of cybernetics as a direction toward the creation of healthy relationships through the healing of paradox and the non-dual combination of thought and emotion.

Viktor Frankl
1905 – 1997 CE
Brave and insightful concentration camp survivor
A survivor of multiple Nazi concentration camps that claimed the lives of his mother, wife, and brother; Frankl developed a psychological approach—logotherapy—based on vivid personal experiences rather than hypothetical theories. He watched how people’s ability to survive in the most horrendous situations correlated with the degree of meaningfulness they could discover as well as seeing how this mirrored his own ability to live through and survive this almost unimaginable suffering. Before his concentration camp experiences he had already focused his work on depression and suicide which successfully prevented even one Viennese student suicide in 1931. After the war, he became an important inspiration for the humanistic psychology movement, wrote 39 books translated into 49 languages, received 29 honorary Ph.D. degrees and taught in locations all over the world. He convincingly debunked the still prevalent deception of finding happiness in relaxation, vacations, and retirement; and pointed instead toward the struggles of meeting challenges, working toward goals, and—most importantly—projects that make the world a better place.

Grace Hopper (Grace Brewster Murray Hopper )
1906 – 1992 CE
Computer programming pioneer "Grandma COBOL,” US Navy admiral nicknamed "Amazing Grace,” IT goodwill ambassador, and recipient of 40 honorary university degrees; Hopper balanced a disciplined and conventional external with a fiercely independent, irreverent, and creative inner force. Her work and belief that computer code could be written in English led to the development of the early programming language, COBOL that’s still in use today. One of the oldest active duty officers in the US Navy’s history, she served for over 42 years and received the National Medal of Technology, the Presidential Medal of Freedom, and numerous awards and honors. While her team was working on an early computer in 1947, they discovered a problem caused by a moth in a relay. This was the physical source of the symbolic term, "debugging."

Mircea Eliade
1907 – 1986 CE
Theologian of the Sacred, philosopher, professor, historian of religion, journalist who “never read newspapers,” and novel writer; Eliade became one of the most influential interpreters of religious experience. As a very conservative youth, he supported far right ideologies; but, during his later life, this support shifted toward the non-Marxist Left and the hippie youth movement. Although an admirer of Gandhi and non-violence, he was accused of antisemitism and support of fascism. He was identified with far-right politics but fired from a University position because of an attack by the far-right press. His theories and descriptions of religious experience (in particular hierophanies and the “Eternal Return”) established paradigms for religious studies still accepted today.

Marshall McLuhan
1911 – 1980 CE
The most controversial and most publicized 20th century English professor, philosopher, founding father of media theory study, visionary “global village” describer who 30 years before it was invented predicted the WWW and coined the term "surfing;” Marshall McLuhan was a popular figure in the 60’s but soon forgotten until the internet proved his predictions and confirmed the ever-increasing cultural influence of technology on culture, business, psychology, and politics. Inspired by G. K. Chesterton to become a Roman Catholic, he credited the Virgin Mary for giving him intellectual guidance. Warning against the dangers of ignoring the consequences of new inventions, his deep historical insights into how new technologies in the past influenced culture give a strong foundation for his analysis of current and soon-to-come technology leading to a “global theater,” a collective identity, "electronic interdependence" ending individualistic print culture, and the creation of a new, global, and ”tribal base.”

E. F. Schumacher
1911 – 1977 CE
The “People's Economist”
While working in Burma during the mid ‘50s, Schumacher developed a set of principles he called “buddhist economics” — emphasizing the idea that people need good work for proper human development. Traveling through many Third World countries, he helped governments create self-reliant economies based on local resources and needs. A pioneer and instigator in creating a philosophy of “appropriate technology,” and known as the “People's Economist,” his economic theory based on wisdom instead of only materialism, became one of the most serious alternatives to the dominant economic theories based on Adam Smith and John Maynard Keynes.

Lewis Thomas
1913 – 1993 CE
Gestaltist of science and art
Innovative blender of poetry with medicine and scientific thought, Thomas broke out of traditional thought patterns to advance more insightful and beneficial approaches to modern psychological, social, and political problems. An early advocate for an ecological approach, he used etymology as a way of creating a holistic understanding of the cultural challenges brought about by new discoveries. A poet himself as well as physician, educator, researcher, and policy advisor; his influence continues through the Lewis Thomas Prize given each year by The Rockefeller University as well as his frequently quoted insights

Huston Smith
1919 – 2016 CE
Born in Suzhou, Huston Smith lived there with his Christian missionary parents until 17 when he moved to the USA where he became not only a religious scholar but a practitioner of his Christian tradition as well as Vedanta, Sufism, and Zen Buddhism for more than 10 years each. A close student of Aldous Huxley, he became an integral part of the Harvard Project and the Center for Personality Research working with Timothy Leary and Ram Das. When the Supreme Court ruled against Native Americans using peyote as a religious sacrament, he took up the cause and helped pass the American Indian Religious Freedom Act amendment. In the 1950s, he helped Martin Luther King break the color barrier at a segregated University and later helped the Dalai Lama come to the USA for the first time. Lifelong advocate of religious synergy, social justice and peace; his work blended theology, mythology, and science.

Timothy Leary
1920 – 1996 CE
Pioneering psychonaut, performing philosopher, and counter-cultural hero
Harvard professor, "performing philosopher,” counter-culture hero, consciousness explorer, and famous psychonaut; Timothy Leary personified the rebel archetype from an early age. He was court-martialed from West Point for refusing to inform on fellow cadets, expelled from the University of Alabama for spending a night in the female dorm, fired from his professorship at Harvard for allegedly missing classes, and during the 60’s and 70’s was imprisoned in 36 different prisons worldwide. President Richard Nixon described him as "the most dangerous man in America.” In 1960, he teamed up with fellow Harvard professor, Richard Alpert (Ram Dass) to launch the first scientific psilocybin research project; and later, with Allen Ginsberg began a campaign to introduce psychedelics and the discovery of higher levels of consciousness to the broader culture. He pioneered research into the benefits of psychedelics in curing alcoholism, inducing religious experiences, and reforming criminals (dropping recidivism rates rates from 60 to just 20%). He won a supreme court marijuana case and—with the support of John Lennon and Yoko Ono—ran for governor of California (Come Together was a Lennon-written campaign song). An early influence on Game Theory, Transactional Analysis, Aldous Huxley, Robert Anton Wilson, and Huston Smith; Leary became a major influence on modern psychology but also created a back-lash that effectively ended psychedelic research until its revival in modern times.

R. D. Laing
1927 – 1989 CE
Shaman, “acid Marxist,” counter-culture high priest, “Elvis of the psyche,” British counterpart to Timothy Leary, friend of Chögyam Trungpa, and psychiatrist to Sean Connery, the Beatles, Jim Morrison, and many other famous 1960’s icons; R. D. Laing was also a serious scholar who challenged orthodox psychology denouncing electro shock, chemical therapy, and the dehumanizing incarceration of the mentally ill. He developed Bateson’s double-bind theory, promoted safe haven centers, and the community-care model that has become today’s norm. Inspired by the Mahasiddha tradition of transmutation and growing the positive in perceived negative, he inspired techniques exemplified by the time he treated a patient with catatonic immobility by helping her get a job as an artist’s model.

Noam Chomsky
1928 CE –
A Jew now banned from Israel but awarded World Peace awards for the promotion of human rights; vilified by corporate interests and the mainstream press but given honorary degrees from over 50 colleges and universities; arrested multiple times for his political activism but one of the single most cited scholars in academic circles; on Nixon's Enemies List and illegally watched by the CIA for many years but considered by progressives “a figure of enlightenment and inspiration;” called by the far right “a hard-boiled anti-American monomaniac” but a foundational pioneer in the fields of cognitive science, linguistic theory, computer science, and evolutionary psychology; Chomsky may be the most important intellectuals alive today.

Mildred Dresselhaus (“the Queen of Carbon”)
1930 – 2017 CE
Growing up impoverished in a dangerous, multiracial neighborhood where teachers in the schools spent most of their time disciplining with little time for teaching; Dresselhausbecame M.I.T.’s first woman full professor, organized their first Women’s Forum, worked hard to encourage more women in science, and now 22% of M.I.T.’s faculty are women. Winning numerous awards including the Presidential Medal of Freedom and a pioneering researcher into the many uses of “buckyball” carbon atoms, she wrote over 1700 scientific papers, co-wrote 8 scientific books, helped discover many new scientific advancements including her research that developed the nonotube - something as strong as steel but one 10,000th the width of a human hair.

Hubert Reeves
1932 CE –
Prolific science popularizer, professor, NASA advisor, and successful Director of Research; Reeves continues to lead a long and productive life dedicated to avoiding scientific pitfalls and encouraging a sane and wise approach to scientific development. A good example of how science can blend and merge with spiritual understanding—like Aldous Huxley's more philosophical concluding realization—Reeves summarizes his scientific understanding with the recognition that the most important priority in life is to be kind and help people.

Jane Goodall
1934 CE –
Adventurer, environmental activist, scientist, pioneering primatologist, and wise gardener; Jane Goodall became UN Messenger of Peace, the world's best expert on chimpanzees, founder of the Roots & Shoots program, and an important influence on young people to choose helping the world over selling out to lucrative careers that plunder the planet. Criticized for changing the chimpanzee social group dynamics, she became an example of McLuhan’s dictum that “every new technology requires a new war” because it disrupts the status quo social order. In this case, the disruption went beyond the chimpanzee social order and also disrupted the human-to-animal and human-to-plant hierarchies. As Stevie Nicks describes her in the song Jane, “There are angels here on earth.”

Jean Houston
1937 CE –
Visionary thinker, philosopher, scholar, historian, and author of 26 books; Jean Houston was trained by Teilhard de Chardin, Eleanor Roosevelt, as well as her father who was Bob Hope’s main comedy writer for 35 years, She’s an active consultant to leaders of 25 countries, worked with the United Nations and UNICEF in more than 100 countries, and helped Hillary Clinton write her book, It Takes a Village. She participated in LSD research before it became illegal and is considered one of the main founders of the Human Potential movement. Her friend and mentor Margaret Mead lived with her the last few years before she died and another lifelong friend, Buckminster Fuller said her “mind should be considered a national treasure.”

Mary Catherine Bateson
1939 CE –
“ Dr. Spock’s first baby,” daughter of Margaret Mead and Gregory Bateson, and after having “the best-documented childhood in the United States,” Mary carried on her parents’ intellectual and anthropological tradition writing and teachings in places like Harvard, George Mason University, and Amherst as well as leading organizations like the Institute for Intercultural Studies in New York. When a freshman in college after attending one of her mother’s lectures with a boyfriend, she lamented the possibility of ever having a good marriage after her mother and father’s example; she agreed to an engagement and wound up married to that same boyfriend for over 50 years.

Paulo Lugari
1944 CE –
Paulo Lugari (1944 - )
Regenerator of a rain forest in a rain-leached, desiccated area without trees, creator of a village (Gaviotas) in a nearly uninhabited area later called by the United Nations “a model of sustainable development,” and known as“the inventor of the world;” Paulo Lugari represents one of the most inspiring stories of human goodness and potential. In 1971 his group of idealistic, challenge-seeking engineers and visionaries moved to a desolate, semi-populated region of Colombia, SA. Today, that once barren land has regenerated a rain forest with millions of trees, sprouted 247 plant species, and established an aquifer that supplies water to over 45,000 people. One of the most hopeful environmental success stories ever told, Gaviotans successfully built a prototype of sustainability in an area ravaged by political terror. Every family has free housing, community meals, and schooling. There are no weapons, no police, no jail or rules, yet they are an oasis of peace.

Jack Weatherford
1945 CE –
Jack Weatherford (1945 - )
Anthropologist, specialist in tribal histories and cultures, and deep thinker about the events and influences of historical events; Weatherford has worked hard uncovering the histories re-written by the victors like the many positive influences of American Indians on US culture, politics, medicine, agriculture, and ecology. This extended to the indigenous cultures of Bolivia, the Amazon, Mongolia and many other little known cultures. For this kind of work, he was awarded Mongolia’s highest national honor for foreigners.

J. Rufus Fears
1945 – 2012 CE
Historian, educator, and serious student of lessons from the past applied to current affairs; Fears was voted Professor of the Year 3 times at the University of Oklahoma and 4 times at Indiana University. His lectures were so popular that none of the lecture halls were large enough to hold the thousands of students wanting to sign up for his classes in History and Political Science. A powerful force animating the relevance and meaningfulness of historical events and people, his last book was titled, Dangerous Delusions: Why We Ignore the Lessons of History at Our Risk. His insights however didn’t seem to extend much beyond the broad into the personal. He ridiculed health advice like exercise and diet, died at only 67 years old.

Kim Stanley Robinson
1952 CE –
One of the greatest living science fiction writers with books translated into 24 languages, The Atlantic called him "the gold-standard of realistic, and highly literary, science-fiction writing." Avid backpacker, sometimes stay-at-home-dad, and cohousing member; his 20+ books portray scientists as heroes with an obligation to ensure good uses for their discoveries and stress environmental themes, sustainability, alternatives to capitalism, and social justice. In 2008, Time magazine gave him a “Hero of the Environment” award.

Steven Pinker
1954 CE –
Humanistic scientist, insightful cultural commentaror
Harvard professor, linguist, cognitive/evolutionary psychologist, humanist, and insightful cultural commentator; Pinker is considered “one of the world's most influential intellectuals.” Translating the significance of new scientific and psychological discoveries into common language, his many books help make these contemporary insights useful in everyday life. Emphasizing the psychology of cooperation and communication, he became a Two-time finalist for the Pulitzer Prize and Humanist of the Year in 2006. His current book, Enlightenment Now helps transmute pessimistic, nihilistic, and negative views into an energized and inspired optimism in relation to both our social and individual states of mind.

Michael Pollan
1955 CE –
Champion for Sustainable Agriculture
Journalist, professor, author, and social activist; Michael Pollan's in-depth and yet intriguing books and articles challenge many of our modern agricultural practices. His historical perspective on agribusiness and how it effects our health, environment, culture, and wellbeing clarifies the problems and gives clear directions toward solutions. He criticized and explained the problems with factory farming, GMOs, and the over-growing of corn effectively enough to provoke a fierce response from the concerned interest groups.

Robert Wright
1957 CE –
Radical centrist, army brat, popular professor, science editor, journalist and prize-winning author; Wright has applied his journalistic skills to translating and interpreting complicated scientific and religious principles. With understanding and insight, his books and articles disentangle the convoluted juxtrapositions interconnecting religion, philosophy, psychology, politics, and science. His decoding of the perspectives of evolutionary psychology and applying them to everyday life offers a valuable key to finding a sane way in these rapidly changing times.
Related Sources (2 sources)
Road Back to Nature by Masanobu Fukuoka
Lives of a Cell: Notes of a Biology Watcher by Lewis Thomas
Quotes about the Scientists Lineage (8 quotes)

“All sciences are only the ordinances and opinions of men, as injurious as profitable, as pestilent as wholesome, as ill as good, in no part perfect, but doubtful and full of error and contention.”
Comments: Click to comment

“Go, wondrous creature, mount where science guides.
Go, measure earth, weigh air, and state the tides;
Instruct the planets in what orbs to run,
Correct old Time, and regulate the sun;
Go, teach Eternal Wisdom how to rule,
Then drop into thyself and be a fool.”
Comments: Click to comment

“There was a thin, small stream of fine learning and of fine thinking up to the 1st century—witness Lucretius and Cicero—but it did not spread into the mass of the people... the broad principles of modern geology shine through the speculations of Lucretius; [but] the true figure to represent the classical Roman attitude to science is not Lucretius, but that Roman soldier who hacked Archimedes to death”
Comments: Click to comment

“I have always had especial hope of those who study the sciences: they ask such intimate questions of nature. Theology possess a vain-gloriousness which places its faith in human theories; but science, at its best, is humble before nature herself. It has no thesis to defend: it is content to knell upon the earth”
Comments: Click to comment

“Every solution bares a new problem. The progress of science has brought new evils with new boons, and its latest victory has given frail minds the power to destroy Western civilization... I morn when I see so much scientific genius dedicated to the art of massacre, so little to the organization of peace... Meanwhile I breathe air and drink water and eat food polluted by the products of science: by the burning of fuels in factories and cars by industrial waste poured into our rivers and seas, by dangerous chemicals used in growing or processing foods or disguising their decay.”
Comments: Click to comment

“a first-rate scientist is never a man condemned to knowledge without insight, sticking to his facts like a mole and unable to look beyond the facts to their meaning, their mystery, and their glory.”
Comments: Click to comment

“Our aim as scientists is objective truth; more truth, more interesting truth, more intelligible truth. We cannot reasonably aim at certainty. Once we realize that human knowledge is fallible, we realize also that we can never be completely certain that we have not made a mistake.”
Comments: Click to comment

“Look at today's scientists who have become the palanquin bearers of rampaging science. They dance about wildly, drunk on the sound of the words, 'high technology.'”
Comments: Click to comment
Comments (0)